 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
Return
to RF Cafe Quiz #48
 This quiz is based on the information presented
in "Introduction to Infrared and Electro-Optical Systems," by Ronald
G. Driggers and Melvin H. Friedman. This quiz is based on the information presented
in "Introduction to Infrared and Electro-Optical Systems," by Ronald
G. Driggers and Melvin H. Friedman.
Graciously provided by Artech House
1. What is the term for light distribution on the image
plane from a point source?
a) Point spread function
The light distribution on the image plane from a point source is called the point
spread function and is abbreviated psf. The psf is never smaller
than a size predicted by diffraction theory and is a manifestation of the wave nature
of the incident radiation. (see page 73)
2. What is the term for when there is a fixed phase relationship
of an EM field between two points in space or two points in time?
d) Coherence
Coherence can be described as a fixed phase relationship of a field between two
points in space or two points in time. (see page 77)
3. What is the term describing "any deviation of light
rays from rectilinear paths which cannot be interpreted as reflection or refraction?"
c) Diffraction
Diffraction is defined by Sommerfield as "any deviation of light rays from rectilinear
paths which cannot be interpreted as reflection or refraction." (see page
83)
4. Which material listed below has the highest total emissivity
(defined as total spectral signature wrt a blackbody)?
a) Snow & graphite
See Table 5.3 on page 131.
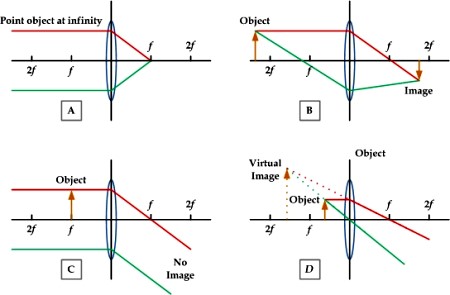 5.
Match the lens ray tracing diagram with its application type. 5.
Match the lens ray tracing diagram with its application type.
a) Magnifying glass _D_
b) Telescope _A_ c) Camera
_B_ d) Search light
_C_
See Figure 7.14 on page 201.
6. What is a 'Cold Shield' as used in electro-optical
systems?
b) A cooled aperture adjacent to the detector plane
The detector is placed within a vacuum enclosure called a Dewar which is usually
the only part of the system that is cooled. Within the Dewar a cooled aperture called
a cold shield is placed adjacent to the detector plane to limit the angle over which
the detectors receive radiation. (see page 253)
7. What are the two general classes of electro-photonic
detectors?
b) Photon (quantum) and thermal
There are two general classes of detectors: photon (or quantum) and thermal detectors.
Photon detector convert absorbed energy into released electrons. Thermal detectors
absorb energy over a broad band of wavelengths. (see page 265)
8. What is a bolometer?
d) A device which varies its electrical resistance depending on the total
electromagnetic power incident upon it.
Bolometer detection is derived from a change in the resistance of the detector
material. (see page 273)
9. What is the modern name of the U.S. Army's former Night
Vision Laboratory (NVL)?*
b) Night Vision & Electronic Sensors Directorate (NVESD)
The [infrared] effort began approximately 50 years ago at the then U.S. Army
Night Vision Laboratory (NVL). Today NVL is known as the U.S. Army Communications &
Electronics Command (CECOM), but is still referred to as NVL in the community and
that acronym. (see page 373)
10. What is Persistent Surveillance?
a) The use of wide-area coverage airborne sensors
A new type of military missions and corresponding sensor has been developed and
fielded in the past few years. The application is called persistent surveillance
(square kilometers) airborne sensor, that provides constant surveillance of a designated
region. (see page 489)
* Note: The reference to West Virginia Senator
Robert C. Byrd in the possible answer list is in jest for the
well-joked-about large number of places in the state that are named after him.
Posted April 16, 2021
|




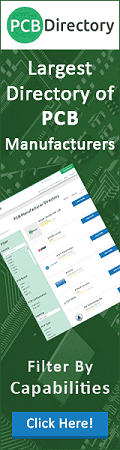












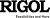



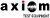







 5.
Match the lens ray tracing diagram with its application type.
5.
Match the lens ray tracing diagram with its application type.