 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
Return to RF Cafe Quiz #16
The subject of Quiz #16 is Antennas. You don't need to be an antenna expert
to score well, but if you do or plan to work with antennas and cannot answer a question
like, "What does dBi, the most often used unit for antenna gain (or directivity),
stand for?," then maybe it is time for some review.
1. What does dBi, the most often used unit for antenna gain (or directivity),
stand for?
c) Decibels of gain relative to an isotropic radiator
An isotropic radiator is theoretically a point source (dimensionless), and therefore
distributes the input power uniformly across the entire spherical volume surrounding
it. Directivity concentrates the input power in a preferred direction, leaving less
power to be radiated in the not-preferred directions.
2. For which region of space does antenna gain normally apply?
b) Far field
Almost without exception, specified antenna gain refers to the far field. The
common sense proof is that if you had two antennas with a gain of, say, 10 dBi,
and placed them face-to-face, you would not realize a gain of 20 dB in signal power
while the path loss would be negligible.
One exception would be NFC (near field communications) antennas which are designed
to use combinations of inductive and/or magnetic coupling to transfer the signal.
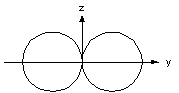
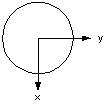 Elevation Pattern
Azimuth Pattern
3. For which type of antenna does the pattern to the right describe?c) 1/2-wave
dipole
See Antenna Patterns page for more patterns.
4. What is the free space impedance that an antenna "sees?"
d) 120p Ω (≈377 Ω)
Z0 = 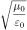 = 120p Ω (μ0 = 4p 10-7 Henries/m, ε0
= 8.854 x 10-12 Farads/m) = 120p Ω (μ0 = 4p 10-7 Henries/m, ε0
= 8.854 x 10-12 Farads/m)
5. What is the name given to the point where the RF input signal interfaces to
the antenna?
b) Feed-point
This is where the signal conductors physically attach to the antenna's radiating
element structure.
 6. Where is the approximate transition point between near field
and far field? 6. Where is the approximate transition point between near field
and far field?
a) λ / (2p)
The explanation is a bit complex, so please see this link on the
Conformity site for details.
7. What is an isotropic radiator?
a) An antenna that radiates equally in all directions
See Q1.
8. Which type of antenna would typically have the highest directivity?
d) Parabolic
Depending on the size, degree of curvature, and the edge properties of the parabolic
dish, gain (directivity, which is generally interchangeable with gain for high efficiencies)
can be very high.
See Antenna Patterns page for gain ranges of various antenna types.
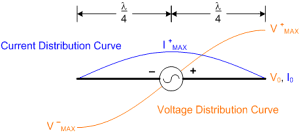
9. On a center-fed 1/2-wave dipole, where is the voltage potential the highest?
b) At the tips (see diagram to right).
Intuitively, at the tips of the antenna the current has nowhere to flow, so I
= 0 there. The 1/2-wave dipole acts like a capacitor where the voltage lags the
current by 90°. As a result, the voltage is at maximum magnitude at the tips.
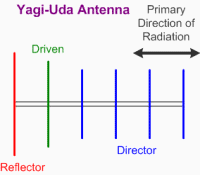 10. Yagi antennas are constructed
of which three types of elements? 10. Yagi antennas are constructed
of which three types of elements?
c) Reflector, driven, and director
The Yagi, or Yagi-Uda, is constructed similar to the one shown to the right.
One or more reflector elements are behind the driven element, and one or more director
elements are in front of the driven element.
Design your own at the
DXZone
website.
Posted July 12, 2022
(updated from original post on 2/12/2005)
|








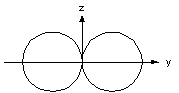
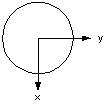


 10. Yagi antennas are constructed
of which three types of elements?
10. Yagi antennas are constructed
of which three types of elements?