 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
Return to RF Cafe
Quiz #23
This quiz challenges your knowledge of digital communications basics. 1.
What is meant by binary frequency shift keying (BFSK)? b) Using two distinctly different
frequencies to represent digital 0s and 1s. For instance in the early days of Bell 300 Baud modems, the "0"
(space) frequency was 1070 Hz and the "1" (mark) frequency was 1270 Hz.
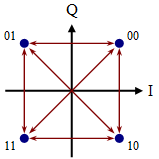 2.
The constellation to the right indicates what type of modulation? 2.
The constellation to the right indicates what type of modulation? a) QPSK QPSK has state
transitions that can either pass through the origin (the diagonal) or directly from state to state (horizontal and
vertical).
3. What is the primary benefit of offset QPSK (O-QPSK) over
QPSK?
c) Constant envelope power. Offset QPSK does not permit the zero transition, which results in a
constant power level (it never goes to zero). The disadvantage is that the method is less efficient because 4 of
the 12 possible transitions are not permitted.
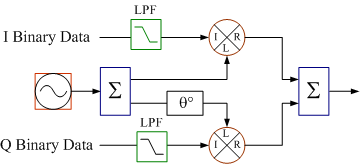 4.
What is the phase shift for the QPSK modulator block diagram to the right? 4.
What is the phase shift for the QPSK modulator block diagram to the right? c) 90° The QPSK
modulator inserts a 90° phase shift at the local oscillator (LO) port of the quadrature (Q) path.
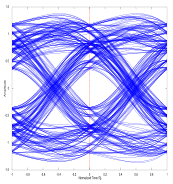 5.
What is the image to the right an example of? 5.
What is the image to the right an example of? d) An eye pattern An eye pattern (also called an eye
diagram) is a time domain representation of the binary state transitions of a digital broadcast (over-the-air or
through a cable). Ideally, the patter closely resemble the modulation scheme's (binary PSK in this case) ideal
constellation diagram. System timing instability, multipath, or other foams of noise result in the type of display
shown. 6. What is the purpose of the lowpass filter (LPF) in the QPSK
modulator shown in Question 4? b) Limits the bandwidth of the transmitted signal It is necessary to
limit the bandwidth of the transmitted signal both to conform to allowed spectral restrictions by governing
authorities (FCC, Ofcom, etc.), to minimize noise content within the system, and to prevent aliasing during the
demodulation/detection process.
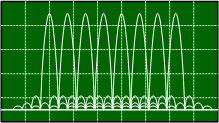 7.
What is the spectrum to the right an example of? 7.
What is the spectrum to the right an example of? a) Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum Frequency
Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) uses a pseudo-random (PR) number sequence to transmit on a fixed set of discrete
frequencies (determined in time by the PR number) in order to minimize the probability of interference with the
signal. The number of frequencies can be just a few, as shown here, or thousands. 8.
Which of the following items affects the bit error rate (BER) of a received signal? d) All the above
All three add uncertainty to the detection process by possibly changing whether the threshold level detector
decides the "bit" is assigned as a "0" or a "1" 9. Which of these issues presents
a problem for zero-IF (direct conversion) receivers? d) All the above Because the local oscillator
(LO) operates at the same frequency as the input RF signal (at the center of the band), the 1x1 (1*LO - 1*RF)
mixer product results in a 0 Hz (DC) signal that gets fed into the digital-to-analog converter, which results in
an uncertainty in making a decision whether the signal bit qualifies as a "0" or a "1." The flicker noise of the
LO diodes is at the baseband frequency, so it also affects uncertainty in binary bit decision making. Finally,
unlike with most well-designed receivers that use an intermittent frequency (IF) prior to the baseband conversion,
a direct conversion receiver will have 2nd-order mixer spurious products that fall inband, so the 2nd-order
intercept point (IP2) will be of concern. 10. What is the Z-transform of the Dirac
delta function, δ[n] ? a) 1 The Dirac delta function is a singularity with an amplitude of 1 at
n=0, and 0 everywhere else. It is used in sampling convolution to determine a signal's value at an instant in
time. Since convolution in the time domain is equivalent to multiplication in the Z domain, a sampled signal is
multiplied by "1" at a determined instant and therefore its amplitude is discovered without a scaling factor. |








 2.
The constellation to the right indicates what type of modulation?
2.
The constellation to the right indicates what type of modulation? 4.
What is the phase shift for the QPSK modulator block diagram to the right?
4.
What is the phase shift for the QPSK modulator block diagram to the right? 5.
What is the image to the right an example of?
5.
What is the image to the right an example of? 7.
What is the spectrum to the right an example of?
7.
What is the spectrum to the right an example of?