Visible Light |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
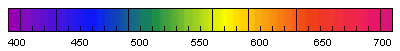
Since a lot of work these days involves properties of light in the visible spectrum (displays, LEDs,
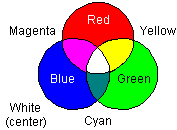
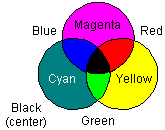
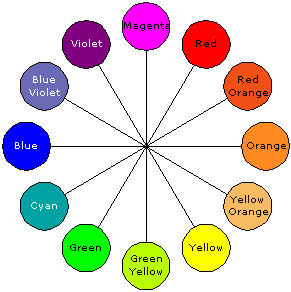
emitters/detectors, etc.), this spectrum chart and color wheel should prove useful. Information on light addition
and subtraction is included in the familiar Venn diagram format. The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to (can be detected by) the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to 750 nm. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 790–400 terahertz. A light-adapted eye generally has its maximum sensitivity at around 555 nm (540 THz), in the green region of the optical spectrum. The spectrum does not, however, contain all the colors that the human eyes and brain can distinguish. Unsaturated colors such as pink, and purple colors such as magenta are absent, for example, because they can only be made by a mix of multiple wavelengths. - Wikipedia Here is the C.I.E. Chromaticity Diagram.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||