 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
Return to RF Cafe Quiz #50
 This
quiz is based on the information presented in
Microstrip Lines and Slotlines, by Ramesh Garg, Inder Bahl, and Maurizio Bozzi. This
quiz is based on the information presented in
Microstrip Lines and Slotlines, by Ramesh Garg, Inder Bahl, and Maurizio Bozzi.
Artech
House graciously provided this book.
Note: Some of these books are available as prizes in the monthly
RF Cafe Giveaway.
1. What is a principal requirement for a transmission structure to be
suitable as a circuit element in a microwave integrated circuit (MIC)? d) It should be planar in configuration.
A planar configuration implies that the characteristics of the element can be determined by the dimensions in
a single plane. (see page 1) 2. What are two consequences of the non-TEM
behavior of microstrip lines? a) Dielectric constant and impedance are functions of frequency
Of these two, the variation of the effective dielectric constant is more significant. (see page 21)
3. Which of the three drawings below represents the highest performance method
of transitioning from coaxial connector to microstrip?
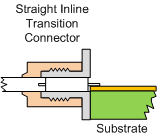 (a) (a)  (b) (b)  (c) (c)
c) Tapered transition With the tapered transition, a 50 Ω impedance is maintained throughout
the transition rather than compensating for discontinuities. (see page 30) 4.
What is full-wave analysis? b) Field analysis not invoking quasi-static approximations
Time-varying electric and magnetic fields must be considered when solving wave equations for microstrip (subject
to boundary conditions) since the system cannot be fully described in terms of static capacitances and inductances.
(see page 59) 5. What happens to the temperature of microstrip as the
frequency increases? c) Dielectric heating causes a temperature rise Substrate (dielectric)
type properties cause varying degrees (pun intended) of heating. Polystyrene, for instance, causes a lot of heating
compared to BeO. (see Figure 2.13 on page 87) 6. What are examples
of discontinuities in microstrip? d) All the above Since discontinuities dimensions are usually
much smaller than the wavelength in microstrip, they may be modeled by lumped element equivalents. (see page
139) 7. Where does the wave propagate in a slotline? a) Along
the slot In a slotline, the wave propagates along the slot with the major electric field component oriented
across the slot in the plane of metallization on the dielectric substrate. (see page 239)
8. What is a Defected Ground Surface (DGS)? c) An intentional deviation from
a continuous flat ground plane. In DGS, the ground plane is intentionally modified to improve the frequency
response of the component. (see page 305) 9. What is the distinguishing
feature of a coplanar waveguide? b) All elements are collocated on the same surface of the substrate
The term "coplanar" is used for those transmission lines/waveguides where all the conductors reside in the same
plane; namely, on the top surface of the substrate. (see page 347) 10.
What is the name given to a configuration whereby two transmission lines are placed parallel to each other and in
close proximity? a) Coupled line In such a configuration there is continuous coupling between
the electromagnetic fields of the two lines. (see page 433) Posted
June 17, 2013
|






 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)


