 All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck! All RF Cafe Quizzes make great fodder for
employment interviews for technicians or engineers - particularly those who are
fresh out of school or are relatively new to the work world. Come to think of it,
they would make equally excellent study material for the same persons who are going
to be interviewed for a job. Bonne chance, Viel Glück, がんばろう,
buena suerte, удачи, in bocca al lupo, 행운을 빕니다,
ádh mór, בהצלחה, lykke til, 祝你好運.
Well, you know what I mean: Good luck!
Click here for the complete list of
RF Cafe Quizzes.
Note: Some material based on books have quoted passages.
Return to RF Cafe
Quiz #54
 This
quiz is based on the information presented in
Microwave Mixer Technology and Applications, by Bert Henderson and Edmar Camargo. This
quiz is based on the information presented in
Microwave Mixer Technology and Applications, by Bert Henderson and Edmar Camargo. Note: Some of these books are available as prizes in the monthly
RF Cafe Giveaway.
1. What is the name given to a receiver circuit whose oscillator
circuit is biased just shy of the oscillation point in order to increase signal sensitivity? d) Regenerative
Positive feedback in the oscillator circuit is adjusted to be just below the point of excitation so that a very
small received signal sends it into oscillation for use in the downconversion and detection circuitry. (see
page 9) 2. What is the name given to a mixer configuration that cancels
out received signal frequencies that are equidistant from the oscillator frequency as the intended signal, but on
the opposite side of the oscillator; i.e., on the opposite equivalent sideband? a) Image reject
If the intended received frequency is f1 and the oscillator frequency if fLO, then the
multiplication (mixing) process (not including harmonics) produces, in the example of a high-side LO, fLO + f1
and fLO - f1 . If f2 = fLO + (fLO + f1)
= 2fLO + f1, then it is the same distance above fLO as f1
is below fLO. Now, substituting f2 into the f1 mixing products yields fLO + f2
and fLO - f2 = fLO + (2fLO + f1)
and fLO - (2fLO + f1) = 3fLO - f1
and fLO + f1. Note that the fLO + f1 term is that
exact same as the original f1 products. Hence, it produces the same output frequency. That is why it
is called the image frequency. (see page 37)

3. What is Error Vector Magnitude (EVM)? c) The difference between the expected
vector magnitude and the measured vector magnitude. As the drawing to the right shows, the Error Vector is
the difference between the ideal vector end point (line V) and the measured vector end point (line Vm). (see
page 67) 4. What is a "cold FET?" d) A FET circuit
without DC bias An example of a cold FET is one used in a frequency mixer circuit where all ports are AC
coupled. (see page 140) 5. Why might a Lange coupler be preferred
over a 3 dB hybrid coupler? c) Wider bandwidth for impedance matching The physical construction
and phasing of its rectangular construction limits the wavelength over which a 3 dB hybrid coupler provides
a good impedance match. (see page 222) 6. What are mixer spurious
products comprised of? c) Large signal LO and small signal RF inputs The LO (local oscillator)
signal is at high enough power to quickly drive the mixer diodes into saturation during the "on" portion of the
cycle while the RF input signal are kept within the more linear conduction region of the diodes. (see page
299) 7. Why does the mechanism of noise generation in a mixer differ than
that of an amplifier? a) Because the device parameters vary in time in response to the LO signal
The large signal LO drive causes the mixer to constantly move through the full operating range of the semiconductor
junctions. (see page 450) 8. Why does a cascode amplifier provide
higher gain than a single stage? c) Because of higher output impedance and higher reverse isolation
The cascode topology also offers a higher frequency of operation due to a reduction in the equivalent input
capacitance. (see page 457)
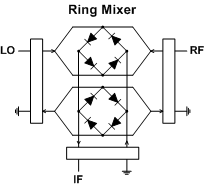  9.
What is the equivalent of a triply-balanced mixer? 9.
What is the equivalent of a triply-balanced mixer? b) Combination of two doubly balanced mixers
A triply-balanced mixer is comprised of two doubly-balanced mixer in parallel, connected between baluns at each
port, as shown in drawing to the right. (see page 322) 10. What
is a major advantage of the Gilbert cell topology? d) It multiplies the input and output currents to
avoid improve linearity d) It multiplies the input and output currents to avoid improve linearity
The Gilbert cell uses transistors to provide current gain for avoiding voltage limitations and thereby improving
linearity. (see page 480) |








 9.
What is the equivalent of a triply-balanced mixer?
9.
What is the equivalent of a triply-balanced mixer?

