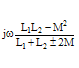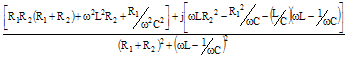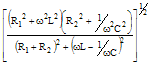Here is an extensive table of impedance, admittance, magnitude, and phase angle
equations (formulas) for fundamental series and parallel combinations of resistors,
inductors, and capacitors. All schematics and equations assume ideal components,
where resistors exhibit only resistance, capacitors exhibit only capacitance, and
inductors exhibit only inductance. My
RF Cafe Espresso Workbook has a worksheet devoted to doing the calculations
for you.
For those unfamiliar with complex numbers, the "±j" operator signifies a phase of ±90°.
Voltage across a capacitor lags the current through it by 90°, so -j is used along
with its capacitive reactance (-j/ωC).
Voltage across an inductor leads the current through it by 90°, so +j is used along
with inductive reactance (jωL).
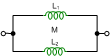
"M" is the mutual inductance between inductors.
"ω" is frequency in radians/second, and is equal to 2π times frequency in cycles/second.
This is probably one of the most comprehensive collections you will find on the
Internet.
Z = R + jX |Z|
= (R2 + X2)½
ϕ
= tan-1(X/R)
Y = 1/Z
 |
R |
R |
0 |
1/R |
 |
jωL |
ωL |
+π/2 |
-j/ωL |
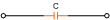 |
-j/ωC |
1/ωC |
-π/2 |
jωC |
 |
jω(L1+L2±2M) |
ω(L1+L2±2M) |
+π/2 |
-j/[ω(L1+L2±2M)] |
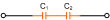 |
-(j/ω)(1/C1+1/C2) |
(1/ω)(1/C1+1/C2) |
-π/2 |
jωC1C2/(C1+C2) |
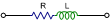 |
R+jωL |
(R2+ω2L2)½ |
tan-1(ωL/R) |
(R-jωL)/(R2+ω2L2) |
 |
R-j/ωC |
(1/ωC)(1+ω2C2R2)½ |
-tan-1(1/ωCR) |
(R+j/ωC)/(R2+1/ω2C2) |
 |
j(ωL-1/ωC) |
(ωL-1/ωC) |
±π/2 |
jωC/(1-ω2LC) |
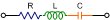 |
R+j(ωL-1/ωC) |
[R2+(ωL-1/ωC)2]½ |
tan-1[(ωL-1/ωC)/R] |
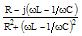 |
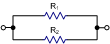 |
R1R2/(R1+R2) |
R1R2/(R1+R2) |
0 |
1/R1+1/R2 |
 |
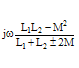 |
 |
+π/2 |
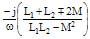 |
 |
-j/ω(C1+C2) |
1/ω(C1+C2) |
-π/2 |
jω(C1+C2) |
 |
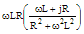 |
ωLR/(R2+ω2L2)½ |
tan-1(R/ωL) |
1/R-j/ωL |
 |
R(1-jωCR)/(1+ω2C2R2) |
R/(1+ω2C2R2)½ |
-tan-1(ωCR) |
1/R+jωC |
 |
jωL/(1-ω2LC) |
ωL/(1-ω2LC) |
±π/2 |
j(ωC-1/ωL) |
 |
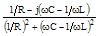 |
[(1/R)2+(ωC-1/ωL)2]-½ |
tan-1[R(1/ωL-ωC)] |
1/R+j(ωC-1/ωL) |
 |
Impedance Z |
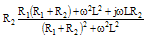 |
| Magnitude |Z| |
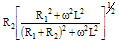 |
| Phase Angle ϕ |
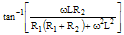 |
| Admittance |
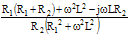 |
 |
Impedance Z |
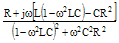 |
| Magnitude |Z| |
 |
| Phase Angle ϕ |
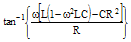 |
| Admittance |
 |
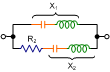 |
Impedance Z |
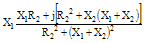 |
| Magnitude |Z| |
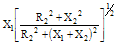 |
| Phase Angle ϕ |
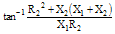 |
| Admittance |
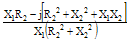 |
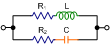 |
Impedance Z |
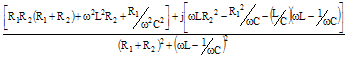 |
| Magnitude |Z| |
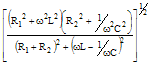 |
| Phase Angle ϕ |
 |
| Admittance |
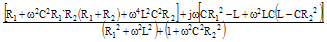 |
 |
Impedance Z |
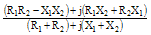 |
| Magnitude |Z| |
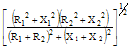 |
| Phase Angle ϕ |
tan-1(X1/R1)+tan-1(X2/R2)-tan-1[(X1+X2)/(R1+R2)] |
| Admittance |
1/(R1+jX1)+1/(R2+jX2) |
Note: Corrections made to RLC Magnitude and Admittance formulas, and to RL||R
Admittance formula on 7/3/2014. Thanks to Bob N. for catching the errors.
(source: Reference Data for Engineers, 1993)
|