When a mixer is used to translate a signal either up or down in frequency, it does so for every spectral component
that lies within the bandwidth of its circuitry. Due to the nonlinear nature of the mixer - a feature necessary
for mixing - harmonics of the input frequencies are generated that also translate up and down with every other
frequency present.
The result is the translation of the fundamental inputs (the local oscillator and the signal of interest),
and also the intermodulation products. Intermod products are
covered in another page on RF Cafe, but here we are concerned with the special case of frequency components that
generate what are termed "image products."
An image frequency is one which lies equidistant from the LO frequency, but on the opposite side, as shown
in the drawing below (down-conversion shown). In this case, we assume the frequency band desired to be translated
down to a lower frequency is the one represented by the orange triangle. It can be seen from the dashed lines
from each of the band regions (orange triangle and green rectangle) that unless some means is provided to prevent
the process, both bands will be translated down to the same set of down-converted frequencies.
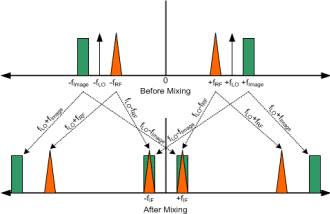
Image Frequency in a Down-conversion
Equations label the lines to indicate the origin of each product. Notice that a negative image of the "positive"
frequencies is shown to the left of 0 Hz (DC). Negative frequencies are often used in order to make the equations
easier to visualize (substitute fLO=-fLO and FImage=-FImage). It prevents
the equations from needing to indicate subtracting a negative number, which is the equivalent of addition.
The fundamental equation for calculating the resulting frequencies from the presence of a local oscillator
(fLO), the intended RF signal (fRF), and the unintended image (FImage), are as
follows:
f = fLO - fRF
f = FImage -
fLO = fRF + 2fIF
Ok, then how do you prevent the image frequency from ending up in the IF band? There are two methods that can be
used alone or together, depending on your system requirements. The first is to use a filter to prevent the image
frequency from ever getting to the mixer input. The other is to use a mixer whose construction is such that a
phasing technique is used to cancel out the image frequency (an image-reject mixer).
See A Graphical Approach to Mixer Spurious Analysis for more
information.
See RF System Cascade Budget Calculation for
more information.