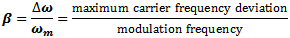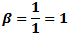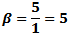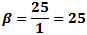|
 Frequency
modulation uses the instantaneous amplitude of a modulating signal (voice, music,
data, etc.) to directly vary the frequency of a carrier signal. Modulation index,
β, is used to describe the ratio of maximum frequency deviation of the carrier to
the maximum frequency deviation of the modulating signal. The concept was pioneered
by Edwin H. Armstrong in the late 1920s and patented in the early
1930s. Frequency
modulation uses the instantaneous amplitude of a modulating signal (voice, music,
data, etc.) to directly vary the frequency of a carrier signal. Modulation index,
β, is used to describe the ratio of maximum frequency deviation of the carrier to
the maximum frequency deviation of the modulating signal. The concept was pioneered
by Edwin H. Armstrong in the late 1920s and patented in the early
1930s.
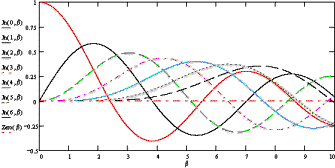
Depending on the modulation index chosen, the carrier and certain sideband frequencies
may actually be suppressed. Zero crossings of the Bessel functions, Jn(β),
occur where the corresponding sideband, n, disappears for a given modulation index,
β. The composite spectrum for a single tone consists of lines at the carrier and
upper and lower sidebands (of opposite phase), with amplitudes determined by the
Bessel function values at those frequencies.
Narrowband FM is defined as the condition where β is small enough to make all
terms after the first two in the series expansion of the FM equation negligible.
Narrowband Approximation: β
= Δω/Ωm < 0.2 (could be as high as 0.5, though)
BW ~ 2ωm
Wideband FM is defined as when a significant number of sidebands have significant
amplitudes.
BW ~ 2Δω
J.R. Carson showed in the 1920's that a good approximation that for both very
small and very large β,
BW ~ 2 (Δω + Ωm)) = 2*Ωm (1 + β)
In the following examples, the carrier frequency is eleven time the modulation
frequency. Red (dashed) lines represent the modulation envelope. Blue (solid) lines
represent the modulated carrier.
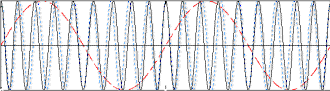
Here, the maximum frequency (fmax) causes a maximum deviation of 1*fmax
in the carrier. From the modulation index formula:
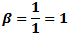
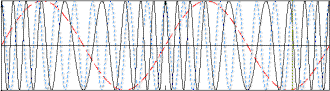
Here, the maximum frequency (fmax) causes a maximum deviation of 5*fmax
in the carrier. From the modulation index formula:
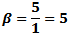
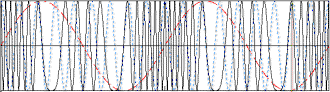
Here, the maximum frequency (fmax) causes a maximum deviation of 25*fmax
in the carrier. From the modulation index formula:
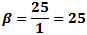
Note: FM waveforms created with MathCAD 4.0 software.
|