
Press Release Archives:
2026 | 2025 |
2024 |
2023 |
2022
2021 |
2020 |
2019 |2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
2015
Content is copyright of company represented. Page format, custom text and
images are RF Cafe copyright - do not distribute. Note: Posting of press releases costs $100 each for non-advertisers.

Sam Benzacar of Anatech Electronics, an RF and microwave filter company,
has published his January newsletter that features his short op-ed entitled
"What 5G Phase 2 Has in Store." He points out that as the Internet and
cellphone service overlap, there is less and less of a distinction between
the two. "When you pore through the information about Release 16, it becomes
obvious that the domains of 'cellular' and IoT will blend to become a single
diverse communications environment comprehensive enough to serve consumer,
industrial, automotive, agricultural, scientific, and other applications.
Today, short-range communication standards such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, and
Thread are used at the edge of the network but Release 16 will allow
cellular to either complement or even replace them eventually." Sam also presents some relevant industry
news items as well.
A Word from Sam Benzacar
What 5G Phase 2 Has in Store
 By Sam Benzacar By Sam Benzacar
Now that 5G is on the way to deployment, the Third Generation Partnership
Project (3GPP) is moving on to Release 16, "5G Phase 2." The new standard covers
an enormous amount of ground, from enhanced coverage and capacity to lower latency,
power consumption, higher reliability, easier deployment, and many other issues.
Taken together, they should make it possible to realize the applications that
will drive 5G for many years.
When you pore through the information about Release 16, it becomes obvious
that the domains of "cellular" and IoT will blend to become a single diverse
communications environment comprehensive enough to serve consumer, industrial,
automotive, agricultural, scientific, and other applications. Today, short-range
communication standards such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, and Thread are used at the
edge of the network but Release 16 will allow cellular to either complement
or even replace them eventually. They will play an even less important role
in autonomous vehicles once they arrive on the scene.
 Release 16 will fully enable all region of the spectrum, focusing on better
use of unlicensed bands in which spectrum sharing is used, such as Citizens
Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in which both licensed and unlicensed entities
share spectrum with existing users, as well as the new allocations at 6 GHz.
The standard will also concentrate on increasing power amplifier efficiency
that is crucial for IoT applications in which sensors and other devices operate
from a battery. Release 16 will fully enable all region of the spectrum, focusing on better
use of unlicensed bands in which spectrum sharing is used, such as Citizens
Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in which both licensed and unlicensed entities
share spectrum with existing users, as well as the new allocations at 6 GHz.
The standard will also concentrate on increasing power amplifier efficiency
that is crucial for IoT applications in which sensors and other devices operate
from a battery.
For the first time it should be possible to provide location services in
three axes that is crucial for public safety services and has eluded many previous
efforts. By combining GPS with cellular-based positioning, Release 16 should
allow location accuracy possibly as low as 3 m and even below 1 m with IoT applications.
To address autonomous vehicles, public safety, and other applications, Release
16 will increase the use of a side link that allows coordinated sensors sharing
as well as higher throughput and lower latency. A variety of new capabilities
will increase reliability potentially up to 99.9% and reduce latency in some
applications below 1 ms over short hops. This is achieved by a technology called
coordinated multipoint (CoMP) that uses multiple transmission and reception
points to create spatial diversity and redundant communication paths.
These are just a few of the capabilities that will soon be integrated within
smartphones, laptops, tablets, and numerous IoT devices. The first Release 16-compliant
chipsets have already been announced, which means they should be finding their
way into various devices sometime next year
Army Develops Quantum Receiver With DC-to 20 GHz Bandwidth
 The Army Research Laboratory has developed a quantum spectrum analyzer that
has an instantaneous bandwidth of DC to 20 GHz. It is based on a Rydberg sensor
that uses laser beams to create Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit.
As the Rydberg atoms react to the circuit's voltage, the device can be used
as a sensitive probe. The device was announced in Physical Review Applied in
the paper "Waveguide-coupled Rydberg spectrum analyzer from 0 to 20 GHz" co-authored
by Army researchers David Meyer, Paul Kunz, and Kevin Cox. One of next steps
will be to better understand how to improve performance as the sensor size is
decreased. The Army Research Laboratory has developed a quantum spectrum analyzer that
has an instantaneous bandwidth of DC to 20 GHz. It is based on a Rydberg sensor
that uses laser beams to create Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit.
As the Rydberg atoms react to the circuit's voltage, the device can be used
as a sensitive probe. The device was announced in Physical Review Applied in
the paper "Waveguide-coupled Rydberg spectrum analyzer from 0 to 20 GHz" co-authored
by Army researchers David Meyer, Paul Kunz, and Kevin Cox. One of next steps
will be to better understand how to improve performance as the sensor size is
decreased.
C-band Auction Nets Nearly $81 billion, Highest Ever
 The C-band auction that closed on January 15 was the highest-grossing auction
ever held by the FCC, with gross proceeds of about $81 billion, passing over
the previous record was of $44.9 billion from the AWS-3 auction in 2015. This
auction offered a total of 280 MHz of 30.7 and 3.98 GHz. In this first phase,
bidders won generic blocks of spectrum, while the assignment phase that began
on February 8 lets them choose for their preferred license assignments. The
biggest bidders, presumably Verizon and AT&T, received much need mid-band
spectrum for 5G, while the much-touted Citizens Broadband Radio Services (CBRS)
auction last summer raised only $4.5 billion. The C-band auction that closed on January 15 was the highest-grossing auction
ever held by the FCC, with gross proceeds of about $81 billion, passing over
the previous record was of $44.9 billion from the AWS-3 auction in 2015. This
auction offered a total of 280 MHz of 30.7 and 3.98 GHz. In this first phase,
bidders won generic blocks of spectrum, while the assignment phase that began
on February 8 lets them choose for their preferred license assignments. The
biggest bidders, presumably Verizon and AT&T, received much need mid-band
spectrum for 5G, while the much-touted Citizens Broadband Radio Services (CBRS)
auction last summer raised only $4.5 billion.
Technique Lets 28-GHz Signals Pass Through Windows
 A major impediment to use of millimeter-wave frequencies for 5G is the inability
of signals at these frequencies to penetrate windows. To remedy this, Japan's
NTT DoCoMo has developed a film-like metasurface lens that can be attached to
window surfaces that it claims can guide 28-GHz radio signals received from
outdoors to specific locations indoors. The lens is made from a material that
has many sub-wavelength unit cells arranged periodically on a two-dimensional
surface in a way that signals from outdoors can be received on a window's broad
surface and then propagated to specific focal points inside a building because
in a manner that directs signals to specific focal points indoors with the help
of repeaters and reflectors. The transparent film can cover the entire inside
surface of a window and was designed to be "aesthetically acceptable". The film
does not affect sub-6 GHz signals, so it should not affect the performance of
legacy wireless frequencies. A major impediment to use of millimeter-wave frequencies for 5G is the inability
of signals at these frequencies to penetrate windows. To remedy this, Japan's
NTT DoCoMo has developed a film-like metasurface lens that can be attached to
window surfaces that it claims can guide 28-GHz radio signals received from
outdoors to specific locations indoors. The lens is made from a material that
has many sub-wavelength unit cells arranged periodically on a two-dimensional
surface in a way that signals from outdoors can be received on a window's broad
surface and then propagated to specific focal points inside a building because
in a manner that directs signals to specific focal points indoors with the help
of repeaters and reflectors. The transparent film can cover the entire inside
surface of a window and was designed to be "aesthetically acceptable". The film
does not affect sub-6 GHz signals, so it should not affect the performance of
legacy wireless frequencies.
Green Bank Telescope to Fill Gap from Destroyed Arecibo Facility
The collapse of the Arecibo Telescope last year after being damaged by Hurricane
Maria deprived radio astronomy of a primary observational tool, but a team at
the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is upgrading an existing telescope
at the Green Bank Observatory in West Virginia to partially replace it while
providing more precise images of near-Earth objects. The Green Bank Telescope
is already the world's largest completely steerable radio telescope, but to
reach near the levels of Arecibo's 300-m observing surface, the 100-m Green
Bank telescope requires some major modifications. They are being performed by
NRAO and Raytheon and will increase the radiated power of the telescope to about
500 KW, allowing astronomers to bounce radar signals off objects as far as Uranus
and Neptune.
Getting Ready for 5G:
Anatech Electronics introduce New Ka band 30.5 GHz Waveguide Band Pass Filter.
Featuring a center frequency of 30.5 GHz, a bandwidth of 1000 MHz, an Insertion
Loss 1 dB Max, and a Power Handling is 20 watts.
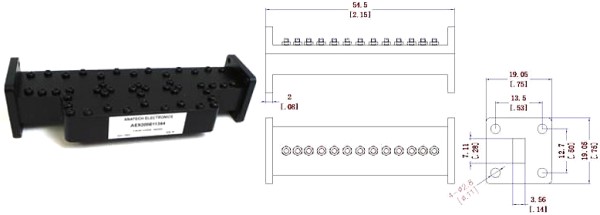
Anatech Electronics Introduces a New Line of Suspended Stripline
and Waveguide Type RF Filters
Check out Our Filter Products



Cavity Band Pass Filters
LC Band Pass Filters Cavity Bandstop/Notch Filter
About Anatech Electronics
Anatech Electronics, Inc. (AEI) specializes in the design and manufacture
of standard and custom RF and microwave filters and other passive components
and subsystems employed in commercial, industrial, and aerospace and applications.
Products are available from an operating frequency range of 10 kHz to 30 GHz
and include cavity, ceramic, crystal, LC, and surface acoustic wave (SAW), as
well as power combiners/dividers, duplexers and diplexers, directional couplers,
terminations, attenuators, circulators, EMI filters, and lightning arrestors.
The company's custom products and capabilities are available at
www.anatechelectronics.com.
Contact:
Anatech Electronics, Inc. 70 Outwater Lane Garfield, NJ 07026
(973) 772-4242
sales@anatechelectronics.com
Posted February 18, 2021
|





 By Sam Benzacar
By Sam Benzacar Release 16 will fully enable all region of the spectrum, focusing on better
use of unlicensed bands in which spectrum sharing is used, such as Citizens
Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in which both licensed and unlicensed entities
share spectrum with existing users, as well as the new allocations at 6 GHz.
The standard will also concentrate on increasing power amplifier efficiency
that is crucial for IoT applications in which sensors and other devices operate
from a battery.
Release 16 will fully enable all region of the spectrum, focusing on better
use of unlicensed bands in which spectrum sharing is used, such as Citizens
Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in which both licensed and unlicensed entities
share spectrum with existing users, as well as the new allocations at 6 GHz.
The standard will also concentrate on increasing power amplifier efficiency
that is crucial for IoT applications in which sensors and other devices operate
from a battery.  The Army Research Laboratory has developed a quantum spectrum analyzer that
has an instantaneous bandwidth of DC to 20 GHz. It is based on a Rydberg sensor
that uses laser beams to create Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit.
As the Rydberg atoms react to the circuit's voltage, the device can be used
as a sensitive probe. The device was announced in Physical Review Applied in
the paper "Waveguide-coupled Rydberg spectrum analyzer from 0 to 20 GHz" co-authored
by Army researchers David Meyer, Paul Kunz, and Kevin Cox. One of next steps
will be to better understand how to improve performance as the sensor size is
decreased.
The Army Research Laboratory has developed a quantum spectrum analyzer that
has an instantaneous bandwidth of DC to 20 GHz. It is based on a Rydberg sensor
that uses laser beams to create Rydberg atoms directly above a microwave circuit.
As the Rydberg atoms react to the circuit's voltage, the device can be used
as a sensitive probe. The device was announced in Physical Review Applied in
the paper "Waveguide-coupled Rydberg spectrum analyzer from 0 to 20 GHz" co-authored
by Army researchers David Meyer, Paul Kunz, and Kevin Cox. One of next steps
will be to better understand how to improve performance as the sensor size is
decreased. The C-band auction that closed on January 15 was the highest-grossing auction
ever held by the FCC, with gross proceeds of about $81 billion, passing over
the previous record was of $44.9 billion from the AWS-3 auction in 2015. This
auction offered a total of 280 MHz of 30.7 and 3.98 GHz. In this first phase,
bidders won generic blocks of spectrum, while the assignment phase that began
on February 8 lets them choose for their preferred license assignments. The
biggest bidders, presumably Verizon and AT&T, received much need mid-band
spectrum for 5G, while the much-touted Citizens Broadband Radio Services (CBRS)
auction last summer raised only $4.5 billion.
The C-band auction that closed on January 15 was the highest-grossing auction
ever held by the FCC, with gross proceeds of about $81 billion, passing over
the previous record was of $44.9 billion from the AWS-3 auction in 2015. This
auction offered a total of 280 MHz of 30.7 and 3.98 GHz. In this first phase,
bidders won generic blocks of spectrum, while the assignment phase that began
on February 8 lets them choose for their preferred license assignments. The
biggest bidders, presumably Verizon and AT&T, received much need mid-band
spectrum for 5G, while the much-touted Citizens Broadband Radio Services (CBRS)
auction last summer raised only $4.5 billion. A major impediment to use of millimeter-wave frequencies for 5G is the inability
of signals at these frequencies to penetrate windows. To remedy this, Japan's
NTT DoCoMo has developed a film-like metasurface lens that can be attached to
window surfaces that it claims can guide 28-GHz radio signals received from
outdoors to specific locations indoors. The lens is made from a material that
has many sub-wavelength unit cells arranged periodically on a two-dimensional
surface in a way that signals from outdoors can be received on a window's broad
surface and then propagated to specific focal points inside a building because
in a manner that directs signals to specific focal points indoors with the help
of repeaters and reflectors. The transparent film can cover the entire inside
surface of a window and was designed to be "aesthetically acceptable". The film
does not affect sub-6 GHz signals, so it should not affect the performance of
legacy wireless frequencies.
A major impediment to use of millimeter-wave frequencies for 5G is the inability
of signals at these frequencies to penetrate windows. To remedy this, Japan's
NTT DoCoMo has developed a film-like metasurface lens that can be attached to
window surfaces that it claims can guide 28-GHz radio signals received from
outdoors to specific locations indoors. The lens is made from a material that
has many sub-wavelength unit cells arranged periodically on a two-dimensional
surface in a way that signals from outdoors can be received on a window's broad
surface and then propagated to specific focal points inside a building because
in a manner that directs signals to specific focal points indoors with the help
of repeaters and reflectors. The transparent film can cover the entire inside
surface of a window and was designed to be "aesthetically acceptable". The film
does not affect sub-6 GHz signals, so it should not affect the performance of
legacy wireless frequencies.








