|
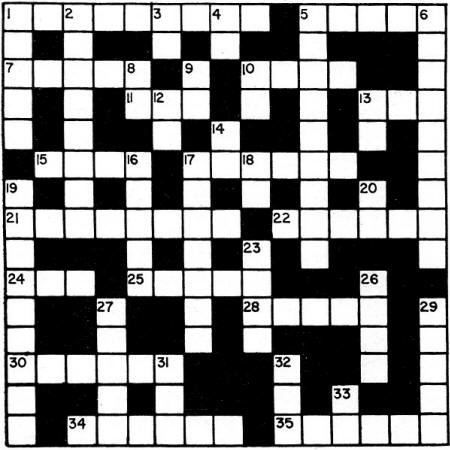
Across
1. Five-grid tube used in superhets.
5. In a beam ____ tube the electrons are focused to achieve greater amplification.
7. Used in gaseous electron tubes.
10. Negative potential applied to tube's control grid.
11. Every TV and scope has one (Abbr.)
13. ____ off is bias voltage at which plate current ceases to flow.
15. Male connectors attached to a tube's base.
17. Resonator associated with magnetron circuits.
21. Electrodes of a tube.
22. ____ triode (tube having two triodes housed in a single envelope).
24. British "treble."
25. Type of light-sensitive cathode.
28. Tube's plate.
30. Extended cut-off vacuum tube.
34. Tube element.
35.Three-element tube.
|
Down
1. Tube's collector.
2. Grid bias voltage's polarity.
3. Transconductance (symbol).
4. Plate current (symbol).
5. An 866-A is one.
6. Tube capable of converting a.c. to d.c.
8. Letters sometimes found on a tube basing diagram.
9. Not a metal tube (Abbr.).
10. Potential and polarity applied to tube's plate and screen grid.
12. Plate resistance (symbol).
13. Letter and sign used to designate point in circuit where the positive terminal
of the grid bias source is connected.
14. Unit of measurement in vacuum-tube current flow.
16. Tube in TV set which moves CRT beam from side to side or up and down.
17. It emits electrons in a tube.
18. Non-gaseous tube (Abbr.).
19. Five-electrode tube with two plates.
20. Class of amplification.
23. Found in output circuit of an electron tube.
26. Concentrated stream of electrons passing from cathode to plate in a power
tube.
27. Tube with two electrodes.
29. Charge resulting from gathering of electrons near the cathode of a tube.
31. ____ inction is the plate potential at which plate current will not flow
in a gaseous tube.
32. ____ uration is condition existing in tube when electron flow within tube
is maximum obtainable by increasing plate voltage or cathode heat.
33. Input power to tube (Abbr.).
|