|
[Go to TOC]
ATTENUATORS / FILTERS / DC BLOCKSATTENUATORS
An attenuator is a passive microwave component which, when inserted in the signal path of a system, reduces
the signal by a specified amount. They normally possess a low VSWR which makes them ideal for reducing load VSWR
in order to reduce measurement uncertainties. They are sometimes used simply to absorb power, either to reduce it
to a measurable level, or in the case of receivers to establish an exact level to prevent overload of following
stages. Attenuators are classified as either fixed or variable and either reflective or non-reflective. The
fixed and variable attenuators are available in both waveguide and coaxial systems. Most of the receivers under 20
GHz use coaxial type attenuators.
FIXED The performance characteristics of a fixed attenuator are: 1. input and output
impedances
2. flatness with frequency 3. average and peak power handling capability 4. temperature dependence
VARIABLE The variable attenuator can be subdivided into two kinds: step attenuator and continuously
variable attenuator. In a step attenuator, the attenuation is changed in steps such as 10 dB, 1 dB or 0.5 dB. In a
continuously variable attenuator, the attenuation is changed continuously and a dial is usually available to read
the attenuation either directly or indirectly from a calibration chart. For a variable attenuator,
additional characteristics should be considered, such as: 1. amount or range of attenuations 2.
insertion loss in the minimum attenuation position 3. incremental attenuation for step attenuator 4.
accuracy of attenuation versus attenuator setting
5. attenuator switching speed and switching noise. REFLECTIVE A reflective attenuator reflects
some portion of the input power back to the driving source. The amount reflected is a function of the attenuation
level. When PIN diodes are zero or reverse biased, they appear as open circuits when shunting a transmission line.
This permits most of the RF input power to travel to the RF output. When they are forward biased, they absorb some
input, but simultaneously reflect some back to the input port. At high bias current, most RF will be reflected
back to the input resulting in a high input VSWR and high attenuation. ABSORPTIVE The VSWR of a
non-reflective (absorptive) PIN diode attenuator remains good at any attenuation level (bias state). This is
accomplished by configuring the diodes in the form of a Pi network that remains matched for any bias state or by
use of a 90E hybrid coupler to cancel the waves reflected to the input connector.
MICROWAVE FILTERS
INTRODUCTION Microwave filters are one of the most important components in receivers. The main functions of
the filters are: (1) to reject undesirable signals outside the filter pass band and (2) to separate or combine
signals according to their frequency. A good example for the latter application is the channelized receiver in
which banks of filters are used to separate input signals. Sometimes filters are also used for impedance matching.
Filters are almost always used before and after a mixer to reduce spurious signals due to image frequencies, local
oscillator feedthrough, and out-of-frequency band noise and signals. There are many books which are devoted to
filter designs. There are many kinds of filters used in microwave receivers, so it is impossible to cover all of
them. If a filter is needed on the output of a jammer, it is desirable to place it approximately half way
between the jammer and antenna vs adjacent to either. The transmission line attenuation improves the VSWR of the
filter at the transmitter. This may allow use of a less expensive filter, or use of a reflective filter vs an
absorptive filter. A filter is a two-port network which will pass and reject signals according to their
frequencies. There are four kinds of filters according to their frequency selectivities. In the examples that
follow, fL = low frequency, fM
= medium frequency, and fH = high frequency. Their names reflect their characteristics, and they are:
1. A low-pass filter which passes the low frequency signals below a predetermined value as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Low-Pass Filter
2. A high-pass filter which passes the high frequency signals above a predetermined value as in Figure 2.

Figure 2. High-Pass Filter
3. A band-pass filter which passes signals between two predetermined frequencies as shown in Figure 3.
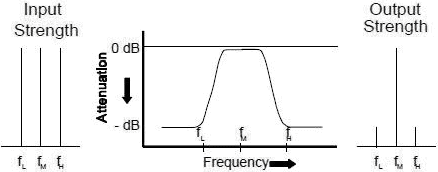
Figure 3. Band-Pass Filter
A band-pass filter with different skirt slopes on the two sides of the pass band is sometimes referred
to as an asymmetrical filter. In this filter the sharpness of the rejection band attenuation is significantly
different above and below the center frequency. One additional note regarding band-pass filters or filters in
general, their performance should always be checked in the out-of-band regions to determine whether or not they
posses spurious responses. In particular they should be checked at harmonics of the operating frequency.
4. A band reject filter (sometimes referred to as a bandstop or notch filter) which rejects signals between two
predetermined frequencies such as high power signals from the aircraft's own radar as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Band-Reject Filter
In general, filters at microwave frequencies are composed of resonate transmission lines or waveguide
cavities that, when combined, reflect the signal power outside the filter frequency pass band and provide a good
VSWR and low loss within the frequency pass band. As such, specifications for filters are maximum frequency, pass
band loss, VSWR, and rejection level at a frequency outside of the pass band. The trade-offs for filters are a
higher rejection for a fixed frequency pass band or a larger frequency pass band for a fixed rejection, which
requires a filter with more resonators, which produce higher loss, more complexity, and larger size.
DC BLOCKS
 DC
Blocks are special connectors which have a capacitor (high pass filter) built into the device. There are three
basic types: DC
Blocks are special connectors which have a capacitor (high pass filter) built into the device. There are three
basic types: 1. INSIDE - The high pass filter is in series with the center conductor as shown in Figure 5.
DC is blocked on the center conductor.
2. OUTSIDE - The high pass filter is in series with the cable shield as shown in Figure 6. 3.
INSIDE/OUTSIDE - A high pass arrangement is connected to both the inner and outer conductors.
 DC
Blocks are ideal for filtering DC, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz from the RF line. DC
Blocks are ideal for filtering DC, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz from the RF line. In general, capacitors with a large
value of capacitance do not have the least loss at microwave frequencies. Also, since capacitance is proportional
to size, a large size produces more capacitance with more inductance. Because of these reasons, D.C. blocks are
typically available with a high pass frequency band starting in the region of 0.1 to 1 GHz.
TERMINATIONS / DUMMY LOADS
A termination is a one-port device with an impedance that matches the characteristic impedance of a given
transmission line. It is attached to a certain terminal or port of a device to absorb the power transmitted to
that terminal or to establish a reference impedance at that terminal. Important parameters of a termination are
its VSWR and power handling capacity. In a receiver, terminations are usually placed at various unconnected ports
of components such as hybrid and power dividers to keep the VSWR of the signal path low. It is extremely important
that the isolated port in a directional coupler and the unused port of a power divider (i.e., only three ports of
a four-way power divider are used) be properly terminated. All of the design considerations of directional
couplers and power dividers are based on the fact that all ports are terminated with matched loads. If an unused
port is not properly terminated, then the isolation between the output ports will be reduced which may severely
degrade the performance of the receiver.
A termination is the terminology used to refer to a low power, single terminal device intended to terminate a
transmission line. Similar devices designed to accommodate high power are generally termed dummy loads.
TERMINATIONS:
Terminations are employed to terminate unconnected ports on devices when measurements are being performed.
They are useful as dummy antennas and as terminal loads for impedance measurements of transmission devices such as
filters and attenuators. The resistive elements in most terminations are especially fabricated for use at
microwave frequencies. Two types are commonly employed: (1) resistive film elements, and (2) molded resistive
tapers. The resistive film is very thin compared to the skin depth and normally very short relative to wavelength
at the highest operating frequency. The molded taper consists of a dissipative material evenly dispersed in a
properly cured dielectric medium. Both forms of resistive elements provide compact, rugged terminations suitable
for the most severe environmental conditions with laboratory stability and accuracy. Terminations should be
properly matched to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line. The termination characteristics of
primary concern are: a. operating frequency range d. VSWR b. average power handling
capability e. size c. operating temperature range f. weight
Many microwave systems employ directional couplers which require terminations on at least one port, and most
have various modes of operation or test where terminations are needed on certain terminals. A matched
termination of a generalized transmission line is ideally represented by an infinite length of that line having
small, but non-zero loss per unit length so that all incident energy is absorbed and none is reflected.
Standard mismatches are useful as standards of reflection in calibrating reflectometer setups and other impedance
measuring equipment. They are also used during testing to simulate specific mismatches which would be encountered
on the terminals of components once the component is installed in the actual system. The following table shows
common mismatches with the impedance that can provide the mismatch.

DUMMY LOADS
A dummy load is a high power one port device intended to terminate a transmission line. They are primarily
employed to test high power microwave systems at full power capacity. Low power coaxial loads are generally termed
terminations and typically handle one watt or less. Most radars or communications systems have a dummy load
integrated into them to provide a non-radiating or EMCON mode of operation, or for testing (maintenance).
Three types of dissipative material are frequently employed in dummy loads: (1) lossy plastic, (2) refractory, and
(3) water.
The lossy plastic consists of particles of lossy material suspended in plastic medium. This material may be
designed to provide various attenuations per unit length but is limited as to operating temperature. It is
employed primarily for low power applications. The refractory material is a rugged substance that may be
operated at temperatures up to 1600EF. It is virtually incapable of being machined by ordinary means but is often
fabricated through diamond wheel grinding processes. Otherwise material must be fired in finished form. Such
material is employed in most high power applications. The dissipative properties of water are also employed
for dummy load applications. Energy from the guide is coupled through a leaky wall to the water which flows
alongside the main guide. Water loads are employed for extremely high power and calorimetric applications.
While dummy loads can operate over full waveguide bands, generally a more economical unit can be manufactured for
use over narrower frequency ranges. The power rating of a dummy load is a complex function dependent upon
many parameters, including average and peak power, guide pressure, external temperature, guide size, air flow, and
availability of auxiliary coolant. The average and peak powers are interrelated in that the peak power capacity is
a function of the operating temperature which in turn is a function of the average power.
Table of Contents for Electronics Warfare and Radar Engineering Handbook
Introduction |
Abbreviations | Decibel | Duty
Cycle | Doppler Shift | Radar Horizon / Line
of Sight | Propagation Time / Resolution | Modulation
| Transforms / Wavelets | Antenna Introduction
/ Basics | Polarization | Radiation Patterns |
Frequency / Phase Effects of Antennas |
Antenna Near Field | Radiation Hazards |
Power Density | One-Way Radar Equation / RF Propagation
| Two-Way Radar Equation (Monostatic) |
Alternate Two-Way Radar Equation |
Two-Way Radar Equation (Bistatic) |
Jamming to Signal (J/S) Ratio - Constant Power [Saturated] Jamming
| Support Jamming | Radar Cross Section (RCS) |
Emission Control (EMCON) | RF Atmospheric
Absorption / Ducting | Receiver Sensitivity / Noise |
Receiver Types and Characteristics |
General Radar Display Types |
IFF - Identification - Friend or Foe | Receiver
Tests | Signal Sorting Methods and Direction Finding |
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) / Reflection Coefficient / Return
Loss / Mismatch Loss | Microwave Coaxial Connectors |
Power Dividers/Combiner and Directional Couplers |
Attenuators / Filters / DC Blocks |
Terminations / Dummy Loads | Circulators
and Diplexers | Mixers and Frequency Discriminators |
Detectors | Microwave Measurements |
Microwave Waveguides and Coaxial Cable |
Electro-Optics | Laser Safety |
Mach Number and Airspeed vs. Altitude Mach Number |
EMP/ Aircraft Dimensions | Data Busses | RS-232 Interface
| RS-422 Balanced Voltage Interface | RS-485 Interface |
IEEE-488 Interface Bus (HP-IB/GP-IB) | MIL-STD-1553 &
1773 Data Bus | This HTML version may be printed but not reproduced on websites.
|








 DC
Blocks are special connectors which have a capacitor (high pass filter) built into the device. There are three
basic types:
DC
Blocks are special connectors which have a capacitor (high pass filter) built into the device. There are three
basic types: DC
Blocks are ideal for filtering DC, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz from the RF line.
DC
Blocks are ideal for filtering DC, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz from the RF line.


