|
[Go to TOC]
PROPAGATION TIME /RESOLUTION
1. ROUND TRIP RANGE:
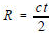 with t =
time to reach target with t =
time to reach target Rules of Thumb
| In one μsec round trip time, a wave travels to and from an object at a distance of: |
The time it takes to travel to and from an object at a distance of: |
| ≈ 150 m ≈ 164 yd ≈ 500 ft ≈ 0.08 NM ≈ 0.15 km |
≈ 1 m ≈ 0.0067 μsec ≈ 1 yd ≈ 0.006 μsec ≈ 1 ft ≈ 0.002 μsec ≈ 1 NM ≈ 12.35 μsec ≈ 1 km ≈ 6.7
μsec |
2. ONE WAY RANGE: R = ct with t = time to reach target
| Time |
Distance Traveled |
|
Distance |
Time it Takes |
| 1 milli sec (ms) |
165 NM |
1 NM |
6.18 μsec |
| 1 micro sec (μs) |
1000 ft |
1 km |
3.3 μsec |
| 1 nano sec (ns) |
1 ft |
1 ft |
1 nsec |
3. UNAMBIGUOUS RANGE
 (DISTANCE
BETWEEN PULSES): (DISTANCE
BETWEEN PULSES):
Normally a radar measures "distance" to the target by measuring time from the last transmitted pulse. If the
interpulse period (T) is long enough that isn't a problem as shown in "A" to the right. When the period is
shortened, the time to the last previous pulse is shorter than the actual time it took, giving a false (ambiguous)
shorter range (figure "B"). Rules of Thumb RNM ≈ 81Pms RKm ≈ 150Pms
Where Pms is PRI in milliseconds
4. RANGE RESOLUTION Rules of Thumb 500 ft per microsecond of pulse width 500 MHz
IF bandwidth provides 1 ft of resolution. 5. BEST CASE PERFORMANCE: The atmosphere limits the
accuracy to 0.1 ft The natural limit for resolution is one RF cycle.
Table of Contents for Electronics Warfare and Radar Engineering Handbook
Introduction |
Abbreviations | Decibel | Duty
Cycle | Doppler Shift | Radar Horizon / Line
of Sight | Propagation Time / Resolution | Modulation
| Transforms / Wavelets | Antenna Introduction
/ Basics | Polarization | Radiation Patterns |
Frequency / Phase Effects of Antennas |
Antenna Near Field | Radiation Hazards |
Power Density | One-Way Radar Equation / RF Propagation
| Two-Way Radar Equation (Monostatic) |
Alternate Two-Way Radar Equation |
Two-Way Radar Equation (Bistatic) |
Jamming to Signal (J/S) Ratio - Constant Power [Saturated] Jamming
| Support Jamming | Radar Cross Section (RCS) |
Emission Control (EMCON) | RF Atmospheric
Absorption / Ducting | Receiver Sensitivity / Noise |
Receiver Types and Characteristics |
General Radar Display Types |
IFF - Identification - Friend or Foe | Receiver
Tests | Signal Sorting Methods and Direction Finding |
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) / Reflection Coefficient / Return
Loss / Mismatch Loss | Microwave Coaxial Connectors |
Power Dividers/Combiner and Directional Couplers |
Attenuators / Filters / DC Blocks |
Terminations / Dummy Loads | Circulators
and Diplexers | Mixers and Frequency Discriminators |
Detectors | Microwave Measurements |
Microwave Waveguides and Coaxial Cable |
Electro-Optics | Laser Safety |
Mach Number and Airspeed vs. Altitude Mach Number |
EMP/ Aircraft Dimensions | Data Busses | RS-232 Interface
| RS-422 Balanced Voltage Interface | RS-485 Interface |
IEEE-488 Interface Bus (HP-IB/GP-IB) | MIL-STD-1553 &
1773 Data Bus | This HTML version may be printed but not reproduced on websites.
|




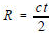 with t =
time to reach target
with t =
time to reach target (DISTANCE
BETWEEN PULSES):
(DISTANCE
BETWEEN PULSES):


