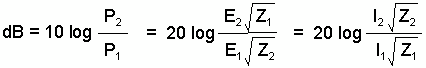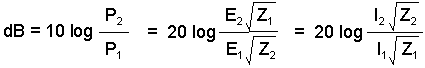|
[Go to TOC]
Decibel (dB)
The Decibel is a subunit of a larger unit called the bel. As originally used,
the bel represented the power ratio of 10 to 1 between the strength or intensity
i.e., power, of two sounds, and was named after Alexander Graham Bell. Thus a power
ratio of 10:1 = 1 bel, 100:1 = 2 bels, and 1000:1 = 3 bels. It is readily seen that
the concept of bels represents a logarithmic relationship since the logarithm of
100 to the base 10 is 2 (corresponding to 2 bels), the logarithm of 1000 to the
base 10 is 3 (corresponding to 3 bels), etc. The exact relationship is given by
the formula
[1] Bels = log(P2/P1)
where P2/P1 represents the power ratio.
Since the bel is a rather large unit, its use may prove inconvenient. Usually
a smaller unit, the Decibel or dB, is used. 10 decibels make one be. A 10:1 power
ratio, 1 bel, is 10 dB; a 100:1 ratio, 2 bels, is 20 dB. Thus the formula becomes
[2] Decibels (dB) = 10 log(P2/P1)
The power ratio need not be greater than unity as shown in the previous examples.
In equations [1] and [2], P1 is usually the reference power. If
P2 is less than P1, the ratio is less then 1.0 and
the resultant bels or decibels are negative. For example, if P2 is one-tenth
P1, we have
bels = log(0.1/1) = -1.0 bels
and dB = 10 log(0.1/1) = -10 dB.
It should be clearly understood that the term decibel does not in itself indicate
power, but rather is a ratio or comparison between two power values. It is often
desirable to express power levels in decibels by using a fixed power as a reference.
The most common references in the world of electronics are the milliwatt (mW) and
the watt. The abbreviation dBm indicates dB referenced to 1.0 milliwatt. One milliwatt
is then zero dBm. Thus P1 in equations [1] or [2] becomes
1.0 mW. Similarly, The abbreviation dBW indicates dB referenced to 1.0 watt, with
P2 being 1.0 watt, thus one watt in dBW is zero dBW or 30 dBm or 60 dBuW.
For antenna gain, the reference is the linearly polarized isotropic radiator, dBLI.
Usually the 'L' and/or 'I' is understood and left out.
dBc is the power of one signal referenced to a carrier signal,
i.e. if a second harmonic signal at 10 GHz is 3 dB lower than a fundamental signal
at 5 GHz, then the signal at 10 GHz is -3 dBc.
The Decibel, Its Use in Electronics
The logarithmic characteristic of the dB makes it very convenient for expressing
electrical power and power ratios. Consider an amplifier with an output of 100 watts
when the input is 0.1 watts (100 milliwatts); it has an amplification factor of
P2/P1 = 100/0.1 = 1000 or a gain of:
10 log(P2/P1) = 10 log(100/0.1) = 30 dB.
(notice the 3 in 30 dB corresponds to the number of zeros in the power ratio)
The ability of an antenna to intercept or transmit a signal is expressed in dB
referenced to an isotropic antenna rather than as a ratio. Instead of saying an
antenna has an effective gain ratio of 7.5, it has a gain of 8.8 dB (10 log 7.5).
A ratio of less than 1.0 is a loss, a negative gain, or attenuation. For instance,
if 10 watts of power is fed into a cable but only 8.5 watts are measured at the
output, the signal has been decreased by a factor of
8.5/10 = 0.85
or
10 log(0.85) = -0.7 dB.
This piece of cable at the frequency of the measurement has a gain of -0.7 dB.
This is generally referred to as a loss or attenuation of 0.7 dB, where the terms
"loss" and "attenuation" imply the negative sign. An attenuator which reduces its
input power by factor of 0.001 has an attenuation of 30 dB. The utility of the dB
is very evident when speaking of signal loss due to radiation through the atmosphere.
It is much easier to work with a loss of 137 dB rather than the equivalent factor
of 2 x 10-14.
Instead of multiplying gain or loss factors as ratios we can add them as positive
or negative dB. Suppose we have a microwave system with a10 watt transmitter, and
a cable with 0.7 dB loss connected to a 13 dB gain transmit antenna. The signal
loss through the atmosphere is 137 dB to a receive antenna with a 11 dB gain connected
by a cable with 1.4 dB loss to a receiver. How much power is at the receiver? First,
we must convert the 10 watts to milliwatts and then to dBm:
10 watts = 10,000 milliwatts and
10 log (10,000/1) = 40 dBm
Then
40 dBm - 0.7 dB + 13 dB - 137 dB + 11 dB - 1.4 dB = -75.1 dBm.
dBm may be converted back to milliwatts by solving the formula: mW = 10(dBm/10)
giving 10(-75.1/10)= 0.00000003 mW
Voltage and current ratios can also be expressed in terms of decibels, provided
the resistance remains constant. First we substitute for P in terms of either voltage,
V, or current, I. Since P=VI and V=IR we have:
P = I2R = V2/R
Thus for a voltage ratio we have
dB = 10 log[(V22/R)/(V12/R)]
= 10 log(V22/V12) = 10 log(V2/V1)2
= 20 log(V2/V1)
Like power, voltage can be expressed relative to fixed units, so one volt is
equal to 0 dBV or 120 dBuV. Similarly for current ratio dB = 20 log(I2/I1)
Like power, amperage can be expressed relative to fixed units, so one amp is
equal to 0 dBA or 120 dBA.
Decibel Formulas (where Z is the general form of R, including
inductance and capacitance)
When impedances are equal:
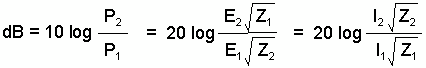
When impedances are unequal: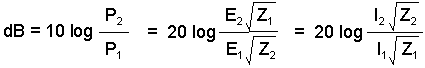
Solutions Without a Calculator
Solution of radar and EW problems requires the determination of logarithms (base
10) to calculate some of the formulae. Common "four function" calculators don't
usually have a log capability (or exponential or fourth root functions either).
Without a scientific calculator (or math tables or a Log-Log slide rule) it is difficult
to calculate any of the radar equations, simplified or "textbook". The following
gives some tips to calculate a close approximation without a calculator.
DECIBEL TABLE

For dB numbers which are a multiple of 10
An easy way to remember how to convert dB values that are a multiple of 10 to
the absolute magnitude of the power ratio is to place a number of zeros equal to
that multiple value to the right of the value 1.
i.e. 40 dB = 10,000 : 1 (for Power)
Minus dB moves the decimal point that many places to the left of 1. i.e. -40
dB = 0.0001 : 1 (for Power)
For voltage or current ratios, if the multiple of 10 is even, then divide the
multiple by 2, and apply the above rules. i.e. 40 dB = 100 : 1 (for Voltage)
-40 dB = 0.01 : 1
If the power in question is not a multiple of ten, then some estimation is required.
The following tabulation lists some approximations, some of which would be useful
to memorize.

You can see that the list has a repeating pattern, so by remembering just three
basic values such as one, three, and 10 dB, the others can easily be obtained without
a calculator by addition and subtraction of dB values and multiplication of corresponding
ratios.
Example 1:
A 7 dB increase in power (3+3+1) dB is an increase of (2 x 2 x 1.26) = 5 times
whereas
A 7 dB decrease in power (-3-3-1) dB is a decrease of (0.5 x 0.5 x 0.8) = 0.2.
Example 2: Assume you know that the ratio for 10 dB is 10, and
that the ratio for 20 dB is 100 (doubling the dB increases the power ratio by a
factor of ten), and that we want to find some intermediate value.
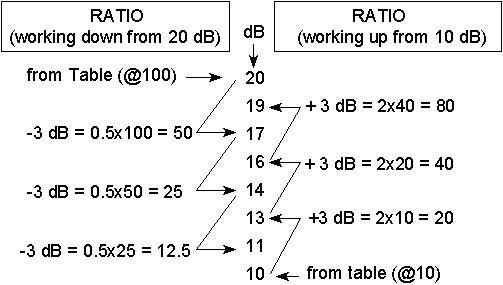
We can get more intermediate dB values by adding or subtracting one to the above,
for example, to find the ratio at 12 dB we can:
work up from the bottom; 12 = 1+11 so we have 1.26 (from table) x 12.5 = 15.75
alternately, working down the top 12 = 13-1 so we have 20 x 0.8(from table) = 16.
The resultant numbers are not an exact match (as they should be) because the
numbers in the table are rounded off. We can use the same practice to find any ratio
at any other given value of dB (or the reverse).
dB as Absolute Units
Power in absolute units can be expressed by using 1 Watt (or1 milliwatt)as the
reference power in the denominator of the equation for dB. We then call it dBW or
dBm. We can then build a table such as the adjoining one.

From the above, any intermediate value can be found using the same dB rules and
memorizing several dB values i.e. for determining the absolute power, given 48 dBm
power output, we determine that 48 dBm = 50 dBm - 2 dB so we take the value at 50
dB which is 100W and divide by the value 1.58 (ratio of 2 dB) to get: 100 watts/1.58
= 63 W or 63,291 mW.
Because dBW is referenced to one watt, the Log of the power in watts times 10
is dBW. The Logarithm of 10 raised by any exponent is simply that exponent. That
is: Log(10)4 = 4. Therefore, a power that can be expressed as any exponent
of 10 can also be expressed in dBW as that exponent times 10. For example, 100 kW
can be written 100,000 watts or 105 watts. 100 kW is then +50 dBW. Another
way to remember this conversion is that dBW is the number of zeros in the power
written in watts times 10. If the transmitter power in question is conveniently
a multiple of ten (it often is) the conversion to dBW is easy and accurate.
Table of Contents for Electronics Warfare and Radar Engineering Handbook
Introduction |
Abbreviations | Decibel | Duty
Cycle | Doppler Shift | Radar Horizon / Line
of Sight | Propagation Time / Resolution | Modulation
| Transforms / Wavelets | Antenna Introduction
/ Basics | Polarization | Radiation Patterns |
Frequency / Phase Effects of Antennas |
Antenna Near Field | Radiation Hazards |
Power Density | One-Way Radar Equation / RF Propagation
| Two-Way Radar Equation (Monostatic) |
Alternate Two-Way Radar Equation |
Two-Way Radar Equation (Bistatic) |
Jamming to Signal (J/S) Ratio - Constant Power [Saturated] Jamming
| Support Jamming | Radar Cross Section (RCS) |
Emission Control (EMCON) | RF Atmospheric
Absorption / Ducting | Receiver Sensitivity / Noise |
Receiver Types and Characteristics |
General Radar Display Types |
IFF - Identification - Friend or Foe | Receiver
Tests | Signal Sorting Methods and Direction Finding |
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) / Reflection Coefficient / Return
Loss / Mismatch Loss | Microwave Coaxial Connectors |
Power Dividers/Combiner and Directional Couplers |
Attenuators / Filters / DC Blocks |
Terminations / Dummy Loads | Circulators
and Diplexers | Mixers and Frequency Discriminators |
Detectors | Microwave Measurements |
Microwave Waveguides and Coaxial Cable |
Electro-Optics | Laser Safety |
Mach Number and Airspeed vs. Altitude Mach Number |
EMP/ Aircraft Dimensions | Data Busses | RS-232 Interface
| RS-422 Balanced Voltage Interface | RS-485 Interface |
IEEE-488 Interface Bus (HP-IB/GP-IB) | MIL-STD-1553 &
1773 Data Bus | This HTML version may be printed but not reproduced on websites.
|